Agile and Waterfall are widely popular project management methodologies, especially in software development. Despite their popularity, they have distinct approaches to how projects are carried out.
The waterfall method follows a step-by-step sequence where each phase must be completed before moving on to the next. In contrast, Agile allows for simultaneous work on different project stages, promoting flexibility and adaptability.
So, how about we dive deep into the debate on Agile vs Waterfall methodologies, comparing their characteristics and applications in project management, especially within software development?
Understanding Agile Project Management
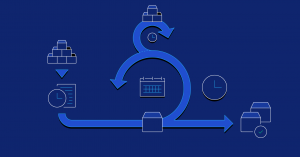
Agile project management is characterized by its emphasis on frequent stakeholder interaction, a high degree of adaptability, and the need for team initiative and adherence to short-term deadlines.
The Agile methodology emerged as a response to the rigidity of Waterfall project management, providing a more dynamic approach to project execution. Agile shines with its flexibility in the ever-evolving landscape of software development, where projects can span years and face significant technological changes.
It readily embraces shifts in direction and incorporates stakeholder feedback throughout the project lifecycle.
In Agile project management, tasks from different phases are often tackled concurrently, focusing on meeting short-term deadlines.
Unlike Waterfall, where project managers typically dictate the course of action, Agile empowers teams to take ownership of their work. This autonomy fosters a sense of accountability and motivation among team members, driving productivity and innovation.
Advantages of Agile Methodology
Agile Methodology in Project Management offers numerous benefits that empower teams to navigate challenges effectively and drive continuous improvement.
- Flexibility: It allows teams to adapt and respond to changes swiftly throughout the project’s lifecycle. This agility enables teams to address evolving requirements and market dynamics effectively.
- Efficiency: By delivering functional products incrementally, Agile promotes efficiency in project execution. Instead of waiting for the entire project to be completed, stakeholders can realize value early on as each iteration adds tangible value.
- Client Engagement: It involves clients as active participants throughout the project, fostering better understanding and satisfaction. Regular interactions and feedback sessions ensure that the final deliverables align closely with the client’s expectations and needs.
- Faster Feedback: Agile methodologies facilitate a quicker feedback cycle, enabling teams to identify issues and course corrections early in the process. This rapid feedback loop ensures that potential risks and challenges are addressed promptly, minimizing project delays.
- Improved Visibility and Accountability: Agile frameworks provide better visibility into project progress, tasks, and priorities. With clear roles, responsibilities, and transparent communication, team members are accountable for their contributions, ensuring alignment toward project goals.
- Continuous Improvement: It encourages a culture of continuous improvement, where teams get to reflect on their processes and practices regularly. Through retrospectives and feedback loops, teams identify areas for enhancement and implement iterative changes to enhance productivity and efficiency over time.
Agile Methodology equips project teams to succeed in today’s business landscape by embracing flexibility, efficiency, client engagement, faster feedback, improved visibility, and continuous improvement, driving impactful results and delivering value to stakeholders.
Disadvantages of Agile Methodology in Project Management

Agile methodology has gained popularity in project management due to its flexibility and adaptability. However, it’s important to acknowledge its drawbacks as well.
Here, we’ll explore some hurdles that project managers may encounter when implementing Agile.
- Complexity: Agile projects can become complex, demanding skilled team members who are adept at navigating the iterative process and managing evolving requirements.
- Lack of Predictability: Unlike traditional methodologies, Agile projects often lack predictability in terms of scope, timeline, and budget. This unpredictability can make it challenging for stakeholders to plan and allocate resources effectively.
- Documentation Challenges: Agile’s emphasis on minimal documentation can pose challenges for future maintenance and knowledge transfer. Without comprehensive documentation, it may be difficult for new team members to understand project history and decisions.
- Overlooked Dependencies: Agile’s focus on short development cycles may lead to overlooking critical path and inter-project dependencies, unlike water methodology. This oversight can result in delays or conflicts down the line.
By understanding and mitigating these challenges with Agile methodology, teams can optimize their processes and achieve successful project outcomes.
Understanding Waterfall Methodology
Waterfall methodology is characterized by its structured approach, where goals and outcomes are predetermined, minimal flexibility, and sequential completion of deliverables is required to advance phases.
This method represents a systematic approach to project management, particularly best for endeavors where project goals are established from the outset. Operating on clear expectations for each project stage, Waterfall mandates the fulfillment of specific deliverables before progress to subsequent phases is allowed.
Waterfall provides a linear framework emphasizing a well-defined roadmap and clear milestones. It is suitable for projects with stable requirements and minimal changes expected throughout development.
Advantages of Waterfall Methodology
While Agile methodology emphasizes flexibility and adaptability, Waterfall methodology offers a structured and sequential approach to project management.
Here, we’ll explore some of the advantages that the Waterfall methodology brings to the table.
- Easy to Understand: Waterfall’s linear process is straightforward to understand, making it easier for teams to grasp project requirements and objectives from the outset.
- Predictability: Unlike Agile, Waterfall provides a defined scope, budget, and timeline at the beginning of the project. This predictability helps stakeholders plan resources and manage expectations more effectively.
- Detailed Documentation: Waterfall requires extensive documentation at each stage of the project, ensuring thorough record-keeping and aiding future maintenance and updates. This documentation also helps in knowledge transfer and mitigates risks associated with team turnover.
- Methodical Design Phase: Waterfall methodology mandates a methodical and well-structured design phase before software development begins. This ensures that project requirements are thoroughly analyzed and understood before moving forward, reducing the likelihood of costly rework later in the project lifecycle.
- Clear Project Phases: Waterfall clearly defines dependencies within each project phase, allowing for better management of resources and schedules. This clarity helps identify potential bottlenecks and mitigate risks early on in the project.
The Waterfall methodology offers a structured and systematic approach to project management, emphasizing predictability, thorough documentation, and clear project phases. While it may not be as flexible as Agile, Waterfall can be highly effective for projects with well-defined requirements and a low tolerance for change.
Disadvantages of Waterfall Methodology

While Waterfall methodology offers structure and predictability, it also comes with its own set of challenges.
Here, we’ll delve into some hurdles project managers may encounter when using the Waterfall approach.
- Lack of Flexibility: Waterfall’s rigid sequential process makes it challenging to accommodate mid-project changes. Any alterations to requirements or scope typically require significant effort and may disrupt the entire project flow.
- Inefficiency: The sequential nature of Waterfall can lead to project delivery delays, especially if issues arise late in the development process. This lack of flexibility can result in missed deadlines and increased project costs.
- Limited Client Involvement: Waterfall often involves clients only at the project’s end, which can lead to misunderstandings and dissatisfaction. Limited client involvement throughout the development process may result in deliverables that do not fully meet their expectations.
- Transition Time Waste: Waterfall methodology may waste time during phase transitions as teams wait for one phase to complete before moving on to the next. This downtime can prolong the overall project timeline and reduce efficiency.
- Communication Overhead: Transitioning between phases in Waterfall incurs additional communication overhead as teams hand off work from one phase to the next. This can lead to delays and misunderstandings if communication channels are not clear or effective.
- Weaker Product Ownership: Waterfall may not promote product ownership and engagement as strongly as Agile. With less frequent feedback loops and client involvement, stakeholders may feel less invested in the project’s success, potentially leading to weaker outcomes.
By understanding these challenges, teams can make informed decisions about the most suitable approach for their projects.
Agile vs Waterfall: Which one should you choose?

When deciding between Agile and Waterfall methodologies for your project, there are several key considerations to remember.
- Consider regulatory requirements: Waterfall is ideal for projects with strict guidelines, ensuring each phase meets criteria, commonly used in safety-centric industries. Agile works best in IT for rapid iteration and parallel progress.
- Consider stakeholder involvement: Agile encourages continuous engagement for feedback and adjustment, while Waterfall’s rigid structure may be better for projects with well-defined requirements.
When to Choose Waterfall Over Agile?
If project managers face situations with specific characteristics, the waterfall methodology may be the preferred choice over agile.
- Clear Project Requirements: Waterfall is optimal when project requirements are well-defined and stable, minimizing the need for extensive rework and changes during development.
- Regulatory Compliance: Projects requiring extensive documentation to meet regulatory standards are better for Waterfall. It emphasizes thorough documentation at each project stage.
- Fixed Budget and Schedule: Waterfall’s precise planning and sequential approach make it ideal for projects with strict budget and timeline constraints, helping to prevent overruns and deviations.
- Limited Client Involvement: When clients cannot be continuously engaged throughout the project and prefer to provide input primarily at the project’s onset, Waterfall’s structured approach with limited client involvement may be advantageous.
- Large or Distributed Teams: Waterfall may be more manageable for large or distributed teams lacking daily interaction. It’s clear task delineation, and sequential workflow facilitates coordination and collaboration.
- Complex, Non-Software Projects: Industries such as construction or aerospace, with distinct phases and sequential execution, may benefit from Waterfall’s linear progression, as it aligns well with the nature of these projects.
- Clear End Product: Projects with well-defined, unchanging objectives, such as building construction or infrastructure development, are better for Waterfall methodology. It ensures a methodical progression towards the clear end product.
In these scenarios, the structured and sequential nature of the Waterfall methodology can offer advantages in managing projects effectively and delivering successful outcomes.
Similarities Between Agile and Waterfall Methodologies
Despite their differences in approach and execution, these methodologies share several key similarities. So, let’s move from Agile vs Waterfall to Agile and Waterfall:
- Goal-oriented: Both methodologies work on delivering high-quality products within predefined time, cost, and scope constraints, prioritizing the achievement of project goals and objectives.
- Development Phases: Both these methodologies follow similar development phases, including planning, designing, developing, testing, and deploying. While the execution may vary (sequential in Waterfall and iterative in Agile), the fundamental stages remain consistent.
- Documentation Importance: While Agile prioritizes working software over comprehensive documentation, both methodologies recognize the importance of documentation for transparency, knowledge transfer, and future maintenance of the project.
- Stakeholder Involvement: Both methodologies emphasize stakeholder engagement throughout the project lifecycle. While Waterfall involves stakeholders primarily at the beginning and end of the project, Agile encourages continuous stakeholder feedback and collaboration.
- Quality Focus: Quality assurance is paramount in both methodologies. While they may employ different approaches to ensure product quality (such as continuous testing in Agile and structured testing phases in Waterfall), both aim for defect-free products that meet customer requirements.
- Project Management Tools: Both Agile and Waterfall methodologies utilize common project management tools such as Gantt charts and Kanban boards to track progress, manage tasks, and visualize workflow, facilitating effective project management and communication within teams.
- Risk Management: Both methodologies recognize the importance of risk management in project execution. Waterfall methodology typically addresses risks early in the project lifecycle. Agile manages risks iteratively throughout the development process, adapting to changes.
Agile and Waterfall methodologies differ but share common goals. They deliver high-quality products, prioritize stakeholder involvement, emphasize quality, use project management tools, manage risks, and aim for customer satisfaction.
Is Combining Agile and Waterfall Possible?
Indeed, merging Agile and Waterfall methodologies, termed the Water-Scrum-Fall model or Agile-Waterfall Hybrid, proves advantageous in specific scenarios. This hybrid approach blends both methods’ strengths to mitigate their drawbacks. It aims to offer Waterfall’s structure and predictability alongside Agile’s adaptability and flexibility.
Essential Features of the Hybrid Approach:
- Initial Planning Phase
- Agile Development Iterations
- Waterfall-style Completion
Conclusion: Agile vs Waterfall
When choosing between Agile and Waterfall methodologies, it’s essential to consider the nature of your project. Waterfall is better if your project outcomes are clear from the start, and adherence to regulations is crucial. Conversely, Agile is best for dynamic projects where speed, experimentation, and collaboration are paramount.
Agile requires a flexible, self-motivated team and frequent stakeholder communication to ensure progress aligns with expectations.
Want to build your teams based on your preferred methodology? Book a call.

Start a Project with Ajackus