Artificial Intelligence, or AI, is seen to revolutionize the transportation industry in profound ways where efficiency and safety are improved while moving towards environmental sustainability, at the same time improving user experiences. The role of AI in transportation industry is said to experience drastic changes in the upcoming years.
The convergence of AI technologies applied in machine learning, computer vision, and predictive analytics comes together to serve smarter, more connected transportation systems. Ample amounts of data are used to optimize everything – from the performance of the vehicles to traffic management and logistics operations. This blog discusses the transformative role of AI in transportation: key technologies, real-world applications, benefits, challenges, and future trends.
Role of AI in Transportation:
AI in transportation is the use of technologies ranging from machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), robotics, and predictive analytics in pursuit of better transport systems in terms of efficiency and safety. These systems heavily lean on huge amounts of data; from sensor data within vehicles, infrastructure, and users, to make real-time decisions and update performances. Whether that be routing autonomous vehicles or predicting traffic patterns, AI can adapt and improve transportation services over time continuously.
Its applications cut across modes of transport through roads, rail, aviation, and maritime to an integrated, seamless, and very efficient transportation ecosystem.
Use of Key Technologies Driving AI in Transportation
1. Machine Learning (ML):
Machine learning algorithms are created to learn from experience. For instance, an AI system may make use of historical data of traffic patterns to optimize a city’s traffic signals or a delivery route to avoid congestion. Over the lifetime of a system, as it gets to see more data, its predictions and optimizations become increasingly accurate, thereby leading to real improvements in efficiency and cost savings.
2. Natural Language Processing (NLP):
NLP enables AI systems to understand and interact with human beings in a conversational manner. In transportation, this can manifest itself in the form of an intelligent virtual assistant or customer service chatbots that the transportation agencies use to respond to queries from passengers in real-time, guide passengers through different routes, and even send warnings when their route is disrupted.
3. Computer Vision:
AI can ‘see’, or interpret visual data, with computer vision; this could include cameras or sensors. This technology is critical both to the cameras and to all the other sensors operating in the autonomous vehicle ‘seen’, such as detect pedestrians, other vehicles, road signs, and other raised obstacles in the road in traffic management systems, or in safety features like collision avoidance systems.
4. Robotic Process Automation (RPA):
RPA is the automation of repetitive, rule-based tasks where systems can perform data entry, report generation, and other forms of records management on their own with zero human intervention. Applications of RPA in transportation include the development of automated ticketing systems, inventory management, and back-end logistics and supply chain processes.
5. Predictive Analytics:
Predictive analytics applies historical data to predict future events. For transportation, it may be useful for predicting traffic patterns, vehicle maintenance needs, or passenger demand. Predictive analytics helps the transportation authority and companies in advance adjustment of schedules and maintaining equipment to prevent issues before they happen.
Applications of AI in the Transportation Industry
1. Autonomous Vehicles
Perhaps the most significant application of AI transport lies in the area of autonomous vehicles, or AVs. Self-driving cars, trucks, and buses use AI to safely drive along roads with no human aid. They rely on a combination of sensors, cameras, GPS, and machine learning algorithms to “see” the world, interpret data, and make decisions in real time.
Real-time Use Case: Waymo
For example, Alphabet Inc’s Waymo subsidiaries have been testing autonomous cars for years with AI systems that make decisions in real-time. Their automobiles use LIDAR, or Light Detection and Ranging, as well as cameras to identify objects around them and distinguish between pedestrians, cyclists, and other cars. Machines also learn through such vehicles to make them better with time as they encounter other driving conditions.
So here, in Waymo, a motto towards eradicating accidents caused by human error, as human error causes 90% of road accidents.
2. Traffic Management Systems
Increasingly, smart traffic management systems use AI to optimize the flow of vehicles through cities. They actually work by analyzing data coming from sensors, cameras, and connected vehicles to adjust real-time traffic lights with a view to reducing congestion and improving overall traffic flow.
Real-time Use Case: Siemens Mobility
Meanwhile, Siemens Mobility is deploying digital twins—the virtual replicas of real infrastructure-enabling cities to test and optimize traffic flows in real-time, adjusting signals on the fly. For instance, their solution for Norwegian railway network uses AI predictive models of train delays and related adjustments in the planning of trains and scheduling, offering better utilization and reduced delay times.
3. Improvement of Public Transportation
There is also a move to optimize public transportation with the aid of machine learning. AI can assess passenger-demand patterns in such a way that schedules, routes, and even the deployment of buses and trains can be changed to minimize waiting times and thereby contribute to efficient service.
Real-time Use Case: Citymapper
Take, for instance, Citymapper-the transportation application-that uses AI to aggregate data based on different public transit systems. For example, it looks at the weather, delayed trains, and even real-time traffic to enable users to arrive better at their destination. Beyond that, machine learning is put to use in predicting when a user will travel; therefore, it can schedule for smarter purposes.
4. AI Docking Assist
AI-based docking and parking technology makes parking even easier and safer for the driver. These generally employ sensors, cameras, and machine learning to enable the car to automatically identify an empty space and park the vehicle using minimal human intervention.
Real-time Use Case: Tesla Autopark
The Autopark feature of Tesla lets the vehicle park itself automatically with the aid of ultrasonic sensors and cameras to determine an available parking space and navigate the vehicle into it. Steering, braking, and acceleration take over to make the driver simply activate the feature and then step back.
5. Predictive Maintenance
AI Predicts when a vehicle or even the infrastructure needs to be serviced. Thus, such would avoid breakdowns and prevent unscheduled repair costs.
Real-time Use Case: GE Transportation
GE Transportation uses AI and predictive analytics to monitor locomotive performance in order that they can predict the point at which the locomotive is going to fail or become mechanical. They can therefore make a maintenance move before a major breakdown with information of this kind.
6. Logistics and Supply Chain Management
AI is revolutionizing logistics and supply chain industries by improving what routes to move through, reducing inventory management, and scheduling deliveries best. With data from traffic flow, weather, and even delivery deadlines, AI algorithms put this information together to determine the most efficient route for a delivery.
7. Safety Upgrades
AI plays a major role in enhancing transport system safety. Advanced driver assistance systems, or ADAS-collision avoidance, lane departure warning, and pedestrian detection, for example-all are spearheaded by AI technologies, including computer vision and machine learning.
Real-time Use Case: Mobileye
Mobileye, owned by Intel, specializes in algorithms of computer vision covering pedestrian, cyclists and other vehicle detection near a car. The system apprises the driver of the probability of collision and, in extreme cases, takes full control of the vehicle to avoid collision, thus ensuring safer roads altogether.
8. Intelligent Parking Systems
AI-equipped parking solutions help drivers quickly locate free parking lots and minimize the need to walk around to find an open space. They evaluate parking lots based on their sensors, cameras, and real-time data and route the next driver to the closest available space.
Real-time Use Case: ParkMobile
ParkMobile is an application using a mobile phone that allows one to find a parking space in real time. The app, through GPS and AI algorithms, locates open parking, hence allowing drivers to book a parking spot and pay for it. It cuts time taken in looking for the parking spot, makes parking a less hectic process, and also makes driving easy.
9. Enhanced Customer Experience
In that light, AI improves the outcome of customer experience based on personalization of services and efficiency in making communications. Whether predicting rider demand or real-time support to a customer, AI is making transportation services more user-friendly.
Real-time Use Case: Uber
Uber uses machine learning algorithms for efficient matching of riders with drivers. Uber can accurately forecast the peak times and locations where demand for rides will be high by analyzing historical data regarding traffic patterns and weather conditions. In this way, it will have enough drivers to take care of customers’ demands. They even make dynamic pricing to balance supply and demand based on varying levels of demand throughout the day.
10. AI in Law Enforcement Transportation Technology
AI is being installed in enforcement vehicles to better operationalize them. With AI, there is better situational awareness in terms of simplifying administrative functions and providing real-time decision support.
Real-time Use Case: AI Technology in Police Cars
Modern police cars are equipped with AI-based technologies like ALPRs that scan plates in real time and cross-check them to some criminals’ databases. They help the officers track high-jacked vehicles, trace suspects, and respond more urgently to incidents thereby enhancing public safety in general.
In contrast, positive merits of AI on transportation include
Therefore, incorporating AI in transportation will have a variety of benefits that may herald a great change for the industry. Some of the most profound impacts include the following:
Efficiency: AI systems optimize route sequences, schedules, and vehicle condition to make transportation more efficient with reduced operational costs.
Improving Safety: ADAS and autonomous vehicles make the transport environment safer by minimizing accidents through the errors of humans.
Cost-savings: Predictive maintenance and AI-based optimization leads to lowered operating and maintenance costs for transport operators while these can be transferred directly to consumers as fees lowered or services enhanced.
Environmental sustainability: AI optimizes route areas to minimize fuel consumption, thereby reducing emissions and catering toward healthy global sustainability.
Customer Experience: The AI gets to personalize and expedite customer services, and, in turn, can enhance satisfaction and raise customer loyalty.
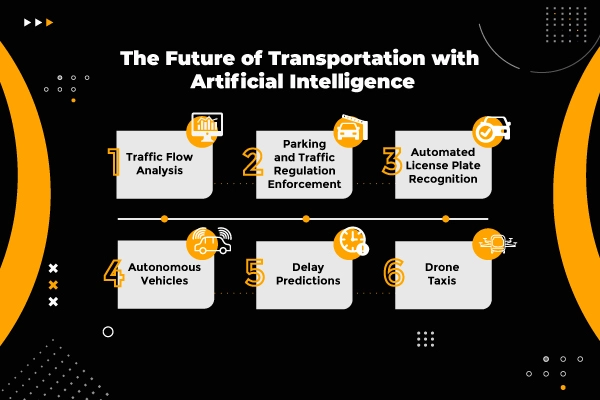
Source: Conure
Challenges in Implementing AI in Transportation
While having several benefits, the implementation of AI in transportation has different hard challenges:
1. Privacy and Security: Huge amounts of personal data may have to be collected and analyzed in order to operate AI, in turn raising the question of privacy and security.
2. Algorithmic Bias: It can, therefore, perpetuate the existing biases unless the data that trains them is not representative or flawed, leading to a result that is unfair.
3. Regulatory Compliance: The rapidly shifting terrain of regulation with regard to AI is going to be an area where transportation companies will struggle to comply further and ensure the ethical use of AI technologies.
4. Implementation Costs: While long-term benefits are high, for smaller companies or municipalities, a prohibitive immediate cost of implementing AI solutions makes them infeasible.
5. Skill Gaps: AI technologies are developing at such a pace that the demand for such technical people creates a tough battle for organizations to find talent for the implementation and maintenance of such AI systems.
Future Trends of AI in Transportation
Transportation AI will be quite promising. Some of the new trends in that field are:
1. Combining AI with Blockchain will enhance the safety and transparency of transportation systems in areas such as logistics and supply chain management.
2. Transport Service Robo-Advisors: In the future, robo-advisors may be used by transport companies to analyze large datasets; hence, providing strategic recommendations for optimization of investment and business operations.
3. Evolving AI in Smart Cities Intelligent cities will be the next drivers of AI and see urban mobility solutions continue to advance with smart traffic management and autonomous public transport.
4. More Advanced Predictive Analytics Future AI systems will provide even more accurate predictions to allow for adjusting transportation systems in real time and thus improving them further.
5. Human-AI Partnership: Future collaborations will be even stronger between human know-how and AI tools, for better decision-making and successful operations in all transportation sectors.
Conclusion:
The role of AI in transportation industry is said to transform by enhancing safety, smoothing efficiency, and improving consumer experience. As technology continues to grow, its reach to the transportation industry would similarly enhance prospects for intelligent, sustainable, and safe transport systems.
However, with challenges brought forward such as data issues, algorithmic bias, and regulatory compliance issues, AI surely promises much to these systems being effective and ethical. Transportation companies, governments and others can create innovation, enhance performance, or increase other value over the long term if all these embrace AI technologies responsibly.
If you are transportation business looking to get started with AI solutions exclusively, Ajackus is here to help you. You can get in touch with us to know more about our offerings. Let’s speak!

Start a Project with Ajackus